The stethoscope has been around in the medical sector for nearly 200 years and is still draped across every physician’s neck or tucked into lab coat pockets. It is a vital instrument that helps healthcare practitioners listen to sounds produced by your heart, lungs, and intestinal tract.
The first stethoscope – an improvised hollow tube, was invented in 1816 by a French physician, René Laennec, who initially felt discomfort about putting his ear on a woman’s chest during the examination. Since then, the stethoscope equips a disc-shaped resonator and two tubes attached with earpieces – a symbol of the medical profession.
Have you ever wondered what a stethoscope does? Well, no worries, this post will explain everything.
How was the Stethoscope introduced?
As we discussed above, the stethoscope was discovered as the first non-invasive tool by a French doctor, Rene Theophile Hyacinthe Laënnec. Earlier, physicians placed their ears directly on the patient to listen to the body’s internal sounds. Later, a wooden tube was created to listen and now it has also evolved dramatically over the years.
But in recent times, there have been calls for frontline workers to ditch the traditional stethoscope and adopt high-tech stethoscope for accurate diagnosis. Today’s stethoscope uses sound amplification and noise cancelling technology to allow healthcare professionals to hear heart and lung sounds and also, store data electronically for future study.
Working Principle of a Stethoscope
A stethoscope is a medical device used to listen to heart, lung, and other body sounds. It encompasses a headset with earpieces, a chest piece, and tubing. Earpieces are attached to the chest piece and allow a doctor or nurse to listen to the patient’s heartbeats and breathing sounds through the tubes.
The device is used to amplify the sound of a patient’s heartbeat and breathing so physicians can hear high to low frequencies more effectively.
Technology Evolution
Even tried-and-tested stethoscopes have been evolved with technological advancements and here’s how:
- Digital stethoscopes now help doctors and nurses to hear heart sounds easily through sound amplification and noise-cancelling technology.
- Telemonitoring tools can help physicians listen to heartbeat remotely, thanks to wireless technology.
- A tool may combine a stethoscope and electrocardiogram (EKG) to let doctors listen and watch heart rhythms at the same time.
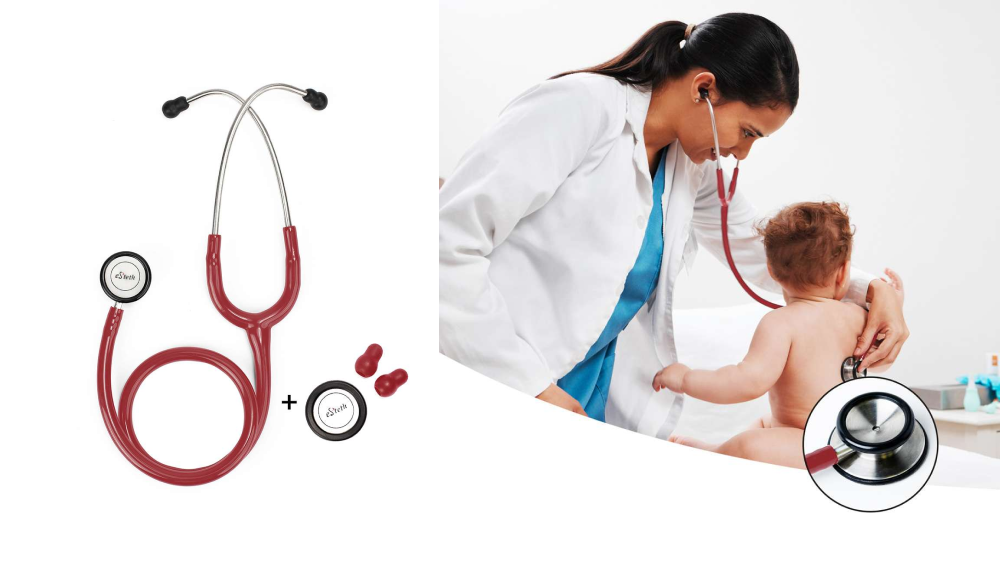
eSteth Stethoscope – Invest in a Life-Saving Medical Device
Thanks to Tech4Life Enterprises, a telemedicine solution provider has brought eSteth Stethoscope in multiple variants, unique designs, and the best sound quality.
eSteth is a reliable brand for stethoscope and serves the purpose it has been designed for. The top picks include eSteth Lite – Digital Stethoscope, eSteth Classic Stethoscope, and eSteth Cardio Stethoscope. All these stethoscopes come in a comprehensive design and eSteth Lite offers high-quality sound amplification up to 100 times to allow medical providers to examine patients easily.
Specifications:
- Flexible tubing – 32-inch long PVC tubing is flexible enough, making it easy to maneuver around patients.
- Clear sound frequency – An ultra-sensitive lightweight chest piece can amplify sound so you can hear low to high frequencies better.
- Additional diagnostic tools – Includes a non-chill ring, extra stethoscope earpieces, and cardiac quality with stainless steel finish to deliver maximum comfort to both physicians and patients.
- Easy sound recording and transfer – You can record sounds with just a push of a button and share data with other specialists during teleconsultation.
If you’re a doctor, nurse, technician, or student, eSteth Stethoscopes can be your go-to solution for accurate assessments and maintaining patient’s well-being. It can be also useful in cardiology and checking heartbeats in an emergency.
As technology is becoming a dominating part of the medical sector, consider investing in eSteth Stethoscopes to aid patients in critical situations.